Unraveling the Mystery: How Visceral Fat Could Be Tied to Alzheimer’s disease
Welcome to a journey into the fascinating world of health and neuroscience, where we explore the hidden connections that shape our well-being. If you’ve ever pondered the importance of body fat beyond just a number on the scale,you’re in for a revelation! Recent research is shedding light on an intriguing culprit often overlooked in discussions about cognitive health—visceral fat. This deep-seated fat,nestled around our organs,has been linked to various health concerns,but new findings suggest it may play a surprising role in the development of alzheimer’s disease. Join us as we delve into the science behind this connection,illuminating how managing visceral fat might not only enhance our physical health but could also hold the key to preserving our precious memories. Buckle up—we’re about to embark on a amiable exploration of how our bodies’ secrets can inform our path to a healthier brain!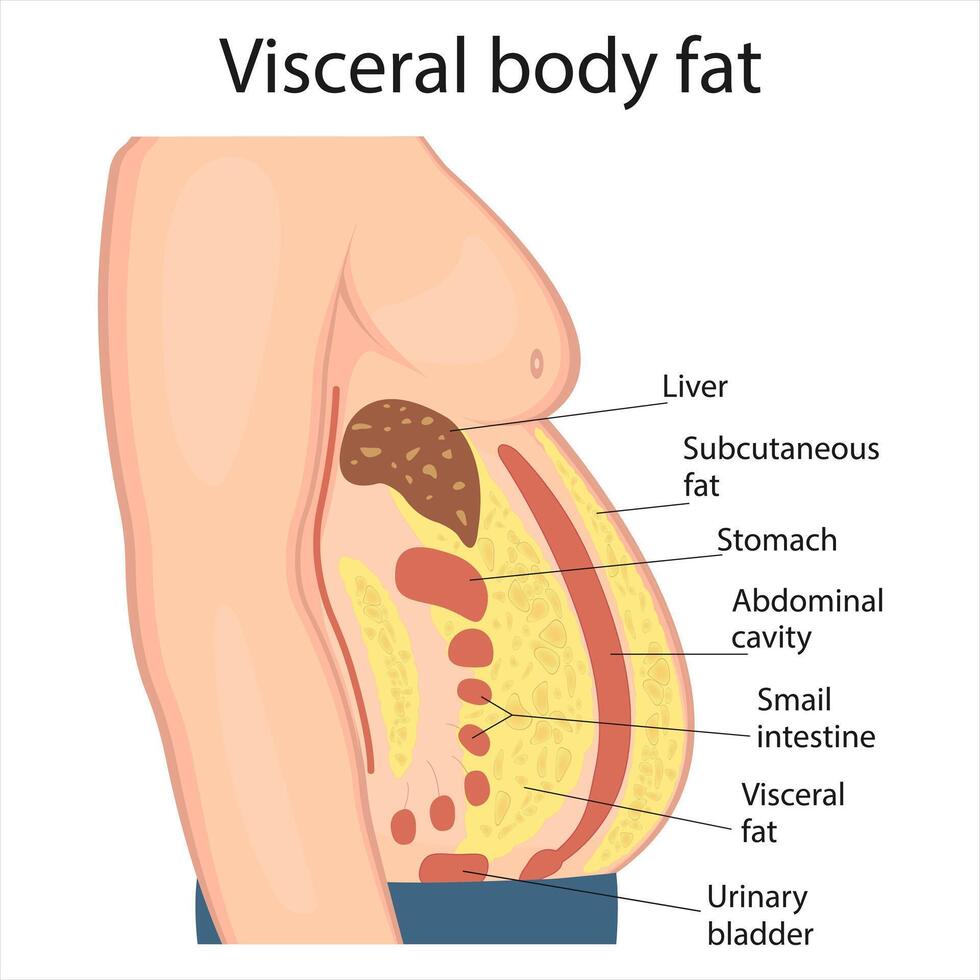
Unraveling the Mystery: How Visceral Fat Links to Alzheimer’s disease
Recent research has illuminated a concerning connection between visceral fat and the development of Alzheimer’s disease. Visceral fat, the type of fat stored around internal organs, is not merely an aesthetic issue; it is a notable player in the realm of cognitive health. Studies suggest that excess visceral fat can lead to increased inflammation and insulin resistance, conditions that are associated with a higher risk of neurodegenerative diseases. The harmful substances released into the bloodstream by visceral fat may contribute to the formation of amyloid plaques and tau tangles in the brain,which are hallmarks of Alzheimer’s pathology.
To understand this complex relationship, it is indeed crucial to consider the following factors:
- Inflammation: Chronic inflammation induced by visceral fat may disrupt neuronal function.
- Insulin Resistance: When the body struggles to utilize insulin properly, it can impair neuronal health.
- Hormonal Changes: Visceral fat can influence hormone levels, affecting brain function.
Furthermore,research indicates that maintaining a healthy level of visceral fat through regular exercise and a balanced diet can potentiate protective effects against cognitive decline.Below, we summarize key findings from recent studies comparing visceral fat levels in normal and Alzheimer’s-affected individuals:
| Study | Participants | Findings |
|---|---|---|
| Study A | 300 Adults | Higher visceral fat correlated with cognitive decline. |
| Study B | 250 Alzheimer’s Patients | Increased inflammation markers linked to visceral fat. |
| Study C | 400 Seniors | Weight loss decreased Alzheimer’s risk significantly. |
The Hidden Dangers: Understanding Visceral Fat and Cognitive Decline
Recent studies have unveiled a troubling link between visceral fat and cognitive decline, particularly in the context of Alzheimer’s disease. Unlike subcutaneous fat, which is stored just beneath the skin, visceral fat wraps around internal organs, making it more metabolically active and potentially risky. This hidden type of fat produces inflammatory substances that can enter the bloodstream, leading to various health issues, including neurodegenerative disorders. The impact of this fat on brain health cannot be overstated, as it may induce a cascade of biochemical changes that compromise cognitive function.
Researchers have identified several mechanisms through which visceral fat may contribute to the onset of Alzheimer’s, including:
- Inflammation: Increased levels of inflammatory markers can affect brain health.
- Insulin Resistance: Linked to metabolic syndrome, this condition may impair brain functions.
- Oxidative Stress: An overload of free radicals can damage neuronal structures.
Understanding these connections is essential for prevention strategies. By managing body fat, adopting a healthier diet, and engaging in regular physical activity, individuals can significantly reduce their visceral fat levels and potentially lower the risk of cognitive decline. Here’s a simple comparison of visceral fat and its implications:
| Type of Fat | Location | Health Risks |
|---|---|---|
| Visceral Fat | Surrounds organs | Inflammation, Alzheimer’s, heart disease |
| Subcutaneous Fat | Under the skin | Less harmful, but still excess may lead to obesity |
Simple Steps to Reduce Visceral Fat for a Healthier Brain
Reducing visceral fat not only helps maintain a healthy weight but also plays a crucial role in supporting brain health. Here are some simple yet effective lifestyle changes you can incorporate to target that stubborn fat:
- Adopt a Balanced Diet: Focus on whole foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Limit processed foods high in sugars and unhealthy fats.
- stay Active: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise each week. Activities like brisk walking, swimming, or cycling can boost metabolism and reduce fat.
- Prioritize Sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night. Insufficient sleep can lead to increased appetite and weight gain.
- Manage Stress: Incorporate stress-relief techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep-breathing exercises to keep cortisol levels in check.
understanding the impact of visceral fat on brain health can motivate you to make these changes. Tracking your progress can also be beneficial:
| Action | Expected Result |
|---|---|
| Follow a Mediterranean diet | Improved cognitive function |
| Exercise regularly | Reduction in visceral fat |
| Prioritize hydration | Enhanced metabolic health |
| Incorporate brain-boosting activities | Stronger neural connections |
Nourishing Your Mind: foods and Habits for a Brighter Future
Embracing the right dietary choices can illuminate your path to cognitive health, especially in light of recent findings linking visceral fat to Alzheimer’s disease development. Incorporating a variety of brain-boosting foods into your meals can significantly enhance your mental clarity and overall well-being. Consider including:
- Fatty fish – Rich in omega-3 fatty acids, thay support brain function and reduce inflammation.
- Berries – Packed with antioxidants, they help combat oxidative stress and improve communication between brain cells.
- Leafy greens – these nutrient-dense vegetables provide essential vitamins that promote neural health.
- Nuts and seeds – A great source of healthy fats and proteins,they are known to aid in brain repair.
Beyond what’s on your plate, cultivating healthy habits can make a world of difference. Regular physical activity not only aids in managing visceral fat but also sparks the release of endorphins, enhancing your mood and cognitive function. Moreover, engaging in activities that challenge your mind, such as puzzles or reading, fosters neuroplasticity—the brain’s ability to adapt and form new connections. Here’s a quick reference of lifestyle choices that can bolster your mental vigor:
| Habit | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Regular exercise | Boosts mood and cognition |
| Mindfulness meditation | Reduces stress and improves focus |
| Sufficient sleep | Enhances memory consolidation |
| Social interaction | Supports emotional well-being |
Wrapping Up
As we wrap up our exploration of the intriguing connection between visceral fat and Alzheimer’s disease, it’s clear that the journey to understanding this complex relationship is far from over. While the findings are sobering,they also open the door to conversations about healthier lifestyle choices that can aid not just our bodies,but our minds as well. By staying active, nurturing balanced diets, and maintaining a keen awareness of our health, we can take proactive steps in the fight against this insidious condition.
so, let’s cherish the moments we have, engage in activities that spark joy, and create a supportive community around our physical and mental well-being. As research continues to unfold,may we remain hopeful and dedicated to uncovering the secrets of our brains.After all, every small step we take today can pave the way for a brighter, healthier tomorrow. Here’s to a future filled with knowledge, compassion, and resilience!
















